Christina's Paper Online!
"Electrochemical and Spectroscopic Studies on σ-Phenyl Ruthenium Complexes"
Christina S. Muck, Michael Linseis, Hannah Welte, Sabrina Weickert, Malte Drescher and Rainer F. Winter
Organometallics, 2018, 37, 13, 2111-2122
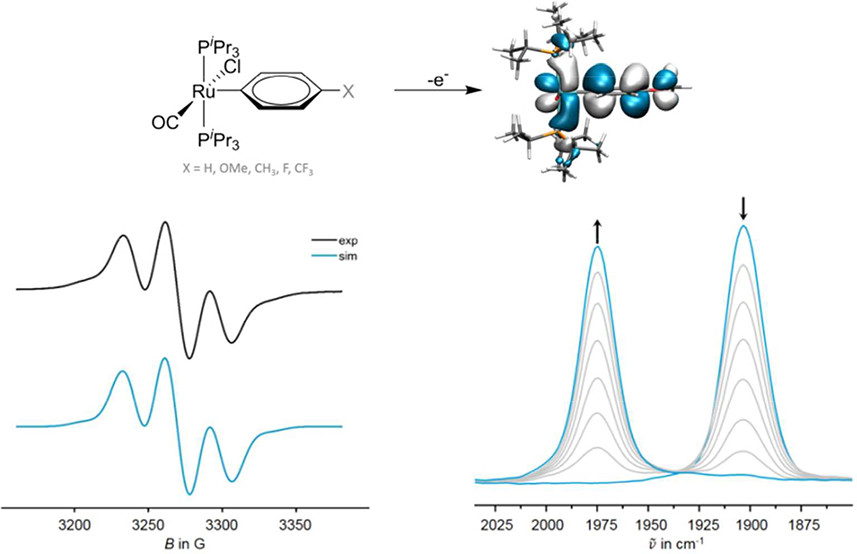
A series of mononuclear σ-phenyl ruthenium complexes Ru(CO)Cl(C6H4-R)(PiPr3)2 (R = OMe, CH3, H, F, CF3) were synthesized and analyzed with respect to their electrochemical and spectroscopic properties. To these ends, cyclic voltammetry, IR, and UV/Vis/NIR spectroelectrochemistry as well as EPR spectroscopy on their one-electron oxidized radical cations were employed. Experimental work is complimented by quantum chemical calculations. Our studies reveal that the σ-phenyl ligand strongly contributes to the HOMO and actively participates in the redox processes. Despite comparatively smaller ligand contributions, the redox potentials, the position of the CO stretch as well as the oxidation induced CO band shifts are more sensitive toward the σ-Hammett parameter of the 4-substituent than for related styryl complexes with the same Ru(CO)Cl(PiPr3)2 metal coligand platform. The comparatively high spin density/positive charge at the 4-position of the phenyl ligand leads to oxidatively induced dehydrodimerization of the radical cation of the parent phenyl complex Ru(CO)Cl(C6H5)(PiPr3)2 (1) to the biphenylene-bridged dinuclear complex [{Ru(CO)Cl(PiPr3)2}2(μ-C6H4–C6H4-4,4′)]n+ (6n+). The latter was identified in spectroelectrochemical experiments and authenticated by independent preparation of neutral 6 and monitoring of its spectroelectrochemical behavior.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.organomet.8b00255
